The Nationwide Institute of Requirements and Know-how (NIST) printed its Synthetic Intelligence Threat Administration Framework (AI RMF 1.0) on January 26, 2023. On the identical day that the NIST AI RMF 1.0 was launched, the White Home introduced its dedication to collaborate and handle accountable AI development below the U.S.-EU Commerce and Know-how Council (TTC) dedication. Each bulletins will shine a vibrant gentle on the necessity for AI governance within the enterprise — now. The EU’s AI Act launch is pending for 2023, which will even have an effect on companies. AI governance just isn’t a nice-to-have anymore.
A Step In The Proper Course …
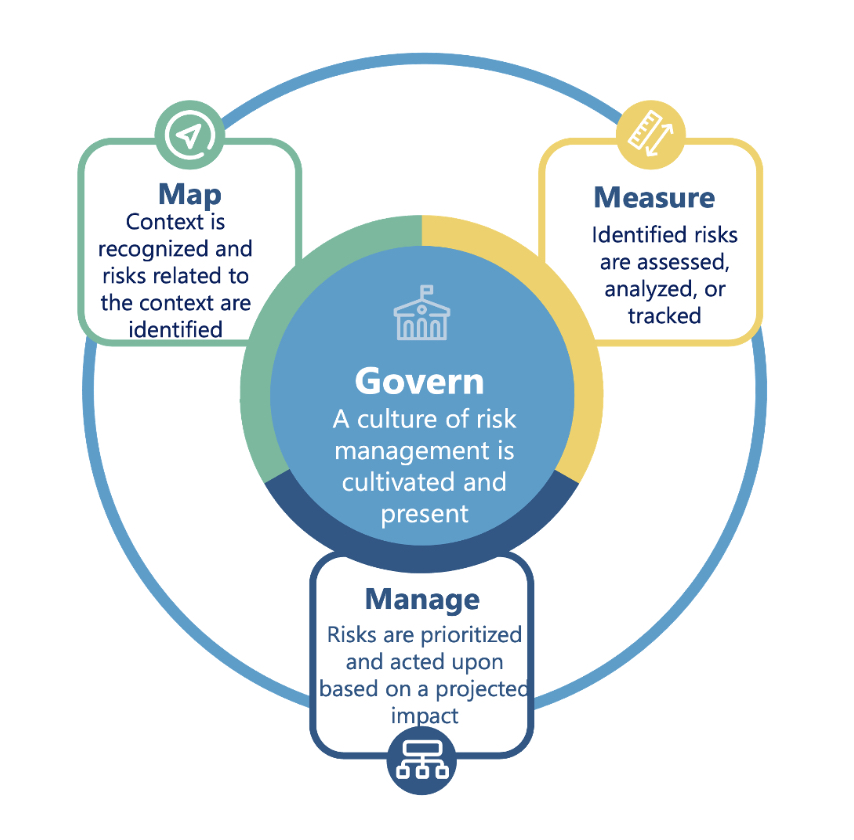
The core tenet of this first-of-its-kind requirements framework is to mitigate hurt to people, to a corporation, or to an ecosystem from inappropriate use of AI whereas additionally reaping the advantages of the promise of this transformative know-how. The framework proposes governance as a tradition supported by mapping context and threat, measuring and analyzing threat, and managing dangers throughout the AI lifecycle. The discharge is well timed as AI laws roll out, new AI know-how comparable to generative AI positive aspects momentum, and enterprises work to make sure that AI is deployed in a accountable and trusted method. The framework can present a complete view and catalog of AI governance capabilities, particularly when it comes to what it may imply for enterprises. Forrester believes that ideas comparable to threat trade-offs, govt participation in AI testing, consideration of third-party AI vetting, and constructing upon present threat frameworks are in line with how we expect that enterprises should method AI governance.
(Picture supply: NIST)
… However Proceed With Warning
Chief information officers and heads of information science must navigate this framework properly to interpret and apply it to their AI governance efforts as a result of it’s nonetheless presently descriptive and never prescriptive. Why? As a result of:
- The conflicts of curiosity are evident. Cross-community collaboration introduced experience and particular pursuits collectively, resulting in contradictions within the framework. Whereas some framework assertions are technically true, they could be disingenuous and inappropriately convey public arguments from areas comparable to the social media and promoting sectors entrance and heart right into a impartial information. Learn Forrester’s analysis on how organizations ought to design and systematically run threat assessments and make use of information clear rooms.
- Mapping and measurement are nonetheless difficult. The framework calls out challenges of opaque and black-box AI, even stating that measurement can be implausible. On the similar time, it states that mapping and measurement is a crucial competency. Enterprises could decide this as a gating issue for AI governance progress or innovation total. Learn Forrester’s analysis on explainable AI and AI equity for strategies to ascertain a context-oriented measurement framework.
- The position of information governance is ambiguous. Knowledge governance doesn’t have an specific reference within the NIST framework, and information stewards are lacking from the record of roles. But Forrester’s analysis finds that when chief information officers (CDOs) and information science leaders champion AI governance, they actively construct upon present information governance practices. As well as, they actively evolve the roles and obligations for AI threat and information integrity. Future updates of the AI RMF might want to handle the dependency between AI and information governance. Learn Forrester’s analysis on information governance to evolve information governance for AI threat.
- The framework is undifferentiated from different governance approaches. The record of AI governance issues is detailed. Much of the framework remains to be generic and like different governance frameworks, nevertheless. Governance applications have a tough historical past in organizations, stymied by lack of adoption; restricted funding and paperwork; slowness; and lacking ROI. Extra work is required to acknowledge challenges and boundaries and supply prescriptive recommendation to succeed the place previous governance has failed. Learn Forrester’s analysis on linked intelligence to modernize AI and information greatest practices.
- Adoption of those requirements stays voluntary. The enterprise case for AI governance is evident below laws. In distinction, norms-based use circumstances associated to areas comparable to free speech or offensive content material are left open to interpretation with out specific penalties to drive AI governance technique. CDOs might want to implement these requirements into their very own governance methods. Learn Forrester’s analysis on trusted information sharing to handle norms-based use circumstances.
It takes appreciable effort and time to make sure the accountable adoption, growth, and deployment of synthetic intelligence. The framework places the AI governance dialog within the enterprise entrance and heart. Be happy to schedule an inquiry to debate methods to apply the framework pragmatically to assist future-proof your AI efforts.