Kenya’s monetary panorama stands as probably the most dynamic in Africa, pushed by fast digitization, excessive cell cash adoption, and continued efforts towards monetary inclusion. The nation is globally acknowledged for the success of M-Pesa, which has reworked the best way Kenyans ship, obtain, and retailer cash since its launch in 2007. Immediately, cell cash platforms are utilized by over 90% of adults, enabling seamless funds, financial savings, and entry to credit score.
In response to the FinAccess Family Survey 2024, 84.8% of Kenyan adults now have entry to formal monetary companies, marking a big milestone in inclusion. The Central Financial institution of Kenya’s Monetary Sector Stability Report 2024 additional notes the rising position of digital lending, with non-bank credit score suppliers and cell mortgage apps changing into key sources of short-term finance, although considerations stay over affordability, information privateness, and shopper safety.
This Kenya-focused examine varieties a part of a broader Sub-Saharan Africa Monetary Providers and Utilization Report, which examined evolving monetary behaviors throughout a number of African markets. Powered by TuuCho; GeoPoll performed the examine by way of GeoPoll’s software and cell internet platform, reaching a complete of two,500 respondents, providing a complete snapshot of how Kenyans entry, use, and understand monetary companies, from cell wallets to conventional banking and rising credit score options. By situating Kenya’s findings throughout the regional context, the report highlights each the nation’s management in digital finance innovation and the continuing have to steadiness accessibility with accountable lending and monetary literacy.
Demographic Overview
The survey gathered responses from a various group of younger Kenyans, with most aged between 25 and 34 years (52%). Males accounted for 64% of respondents and females 36%, with a majority residing in city areas (73%) in comparison with rural areas (27%). By way of revenue, most respondents fall inside decrease to mid-income brackets, reflecting the significance of reasonably priced monetary options. About 34% earn between KES 10,000 and 35,000 per 30 days, whereas 31% earn beneath KES 10,000. A smaller however rising middle-income section, representing 15%, earns between KES 35,000 and 50,000 month-to-month.
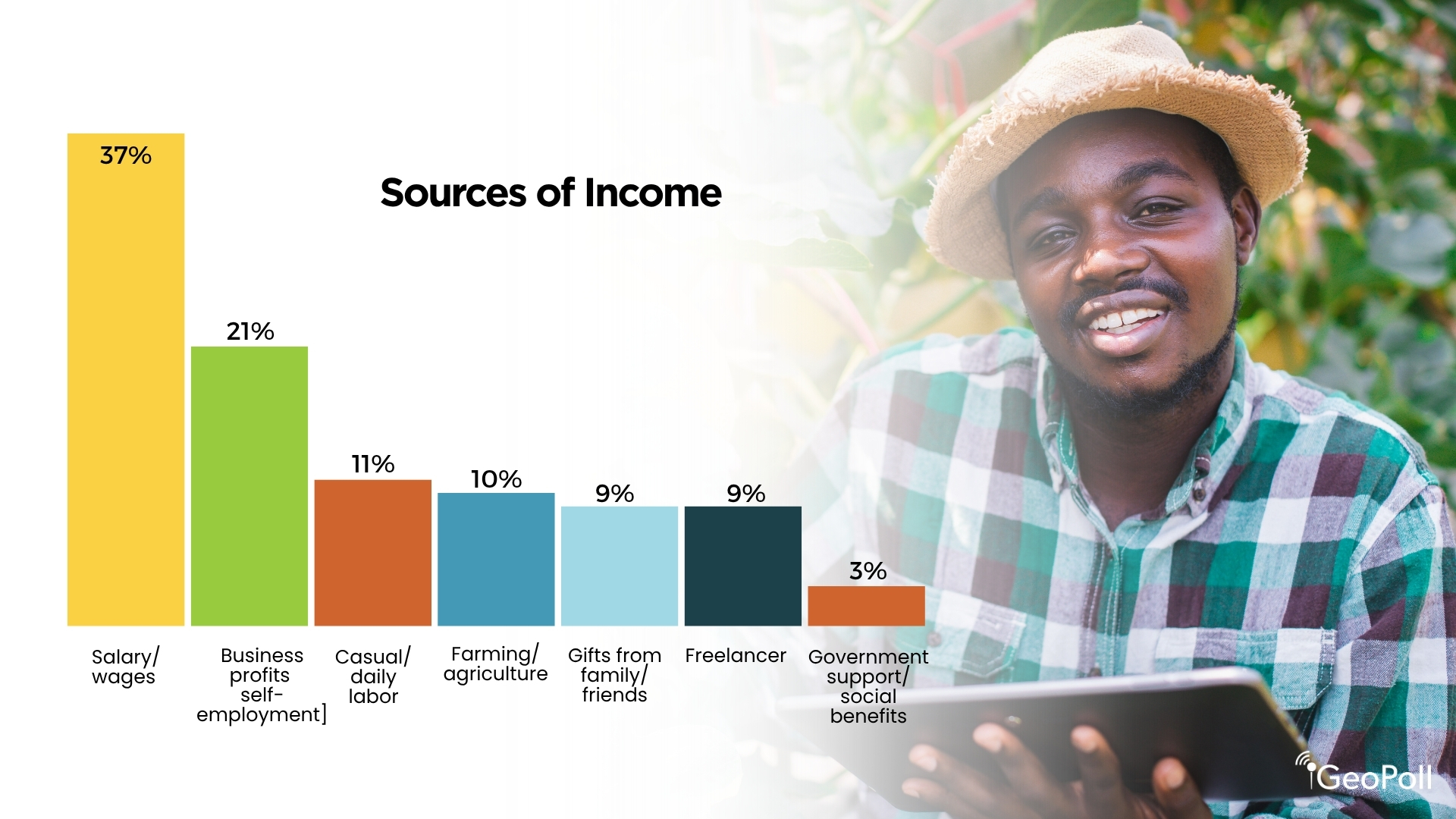
Sources of Earnings
The info signifies that the majority Kenyans derive their revenue from formal employment and small companies, reflecting a combined however evolving labor panorama. A big 37% of respondents earn their main revenue by way of salaries or wages from formal employment, exhibiting the continued significance of structured jobs, notably in city facilities. The second-largest supply of revenue is enterprise earnings or self-employment, reported by 21% of respondents, highlighting Kenya’s sturdy entrepreneurial tradition and the position of micro, small, and medium enterprises in sustaining livelihoods. Informal or day by day labor ranks third at 11%, pointing to a sizeable portion of the inhabitants engaged in casual or short-term work.
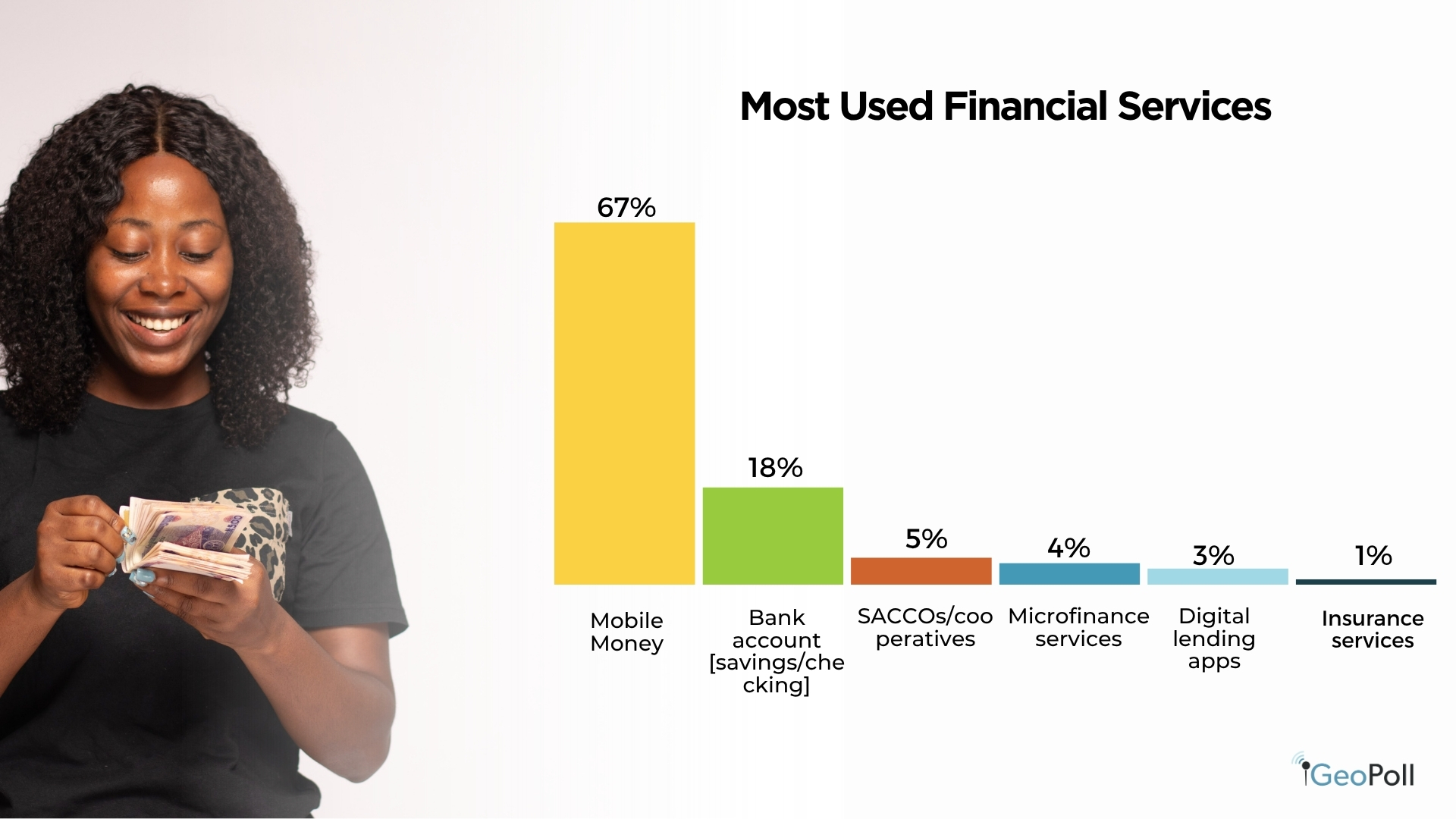
Monetary Service Utilization in Kenya
The findings reveal that cell cash platforms stay the dominant monetary service in Kenya, reflecting their central position in on a regular basis transactions and monetary inclusion. About 67% of respondents reported utilizing cell cash companies resembling M-Pesa, far surpassing all different monetary channels. This demonstrates the continued integration of cell finance into each private and enterprise actions throughout the nation. The second most used service is financial institution accounts (together with financial savings and checking), cited by 18% of respondents, exhibiting that whereas conventional banking stays vital, it lags behind mobile-based options in accessibility and utilization. SACCOs and cooperatives observe distantly at 5%, indicating their area of interest however trusted position, notably in rural and community-based monetary methods. The comparatively low adoption of microfinance companies (4%), digital lending apps (3%), and insurance coverage companies (1%) factors to alternatives for development in formal and digital finance past funds, particularly in credit score, financial savings, and threat safety merchandise.
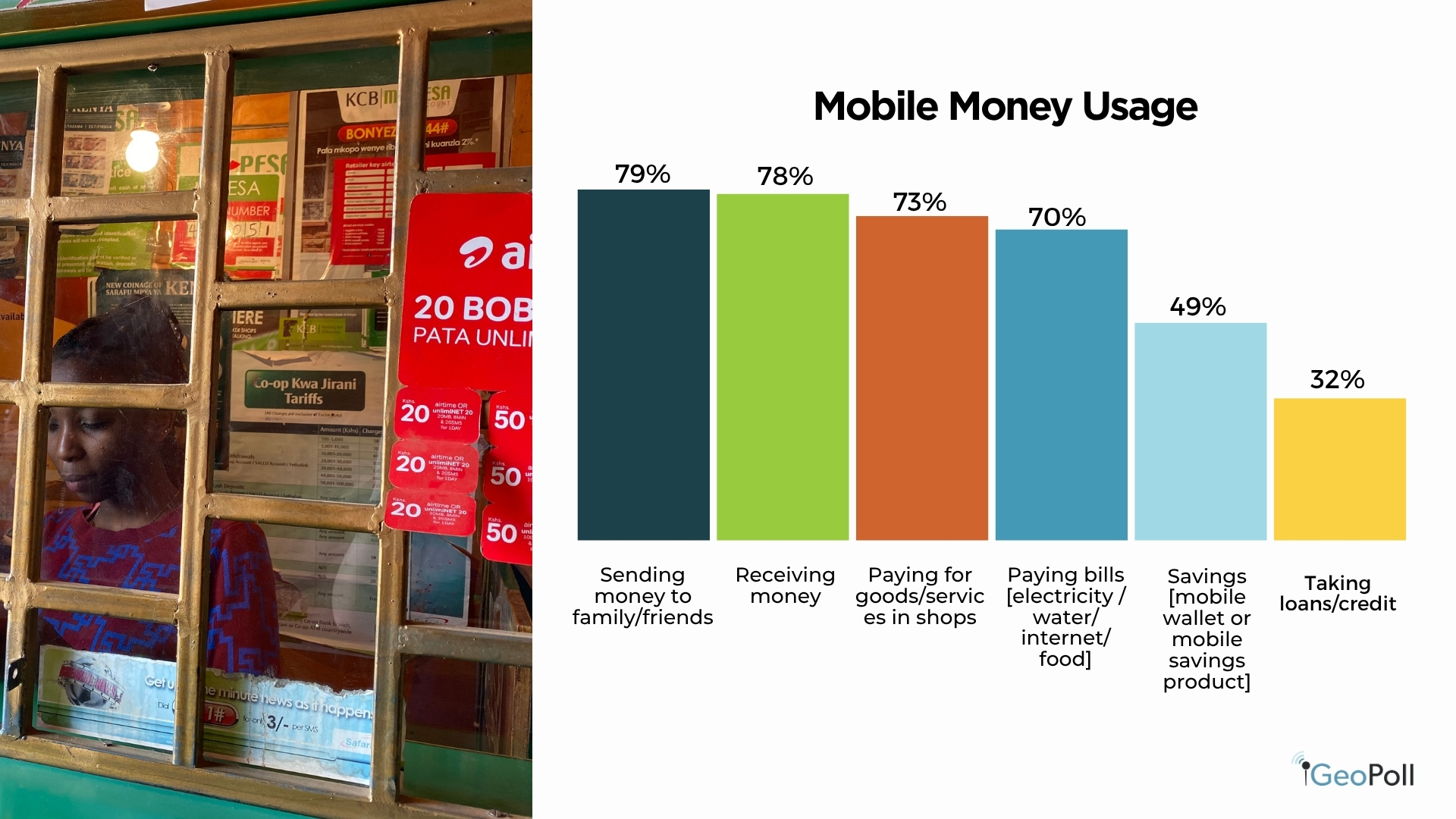
Cellular Cash Utilization in Kenya
Cellular cash continues to outline Kenya’s monetary panorama, reaching near-universal adoption. In response to the survey, an awesome 98% of respondents reported utilizing cell cash companies resembling M-Pesa or Airtel Cash, confirming its place because the nation’s dominant monetary software. This near-total penetration displays how cell wallets have turn into deeply embedded in day by day monetary exercise, bridging gaps in formal banking entry and enabling real-time transactions for hundreds of thousands.

When requested about their principal makes use of of cell cash, Kenyans demonstrated its versatility past easy transfers. The bulk use it for sending (79%) and receiving cash (78%), adopted carefully by paying for items and companies (73%) and settling payments (70%) resembling electrical energy, water, and web. Moreover, almost half (49%) use cell cash for financial savings, whereas 32% depend on it for loans or credit score, reflecting the increasing position of digital finance in assembly broader monetary wants. This reveals that cell cash has developed from a cost platform right into a multifunctional ecosystem supporting each transactional and monetary administration actions.
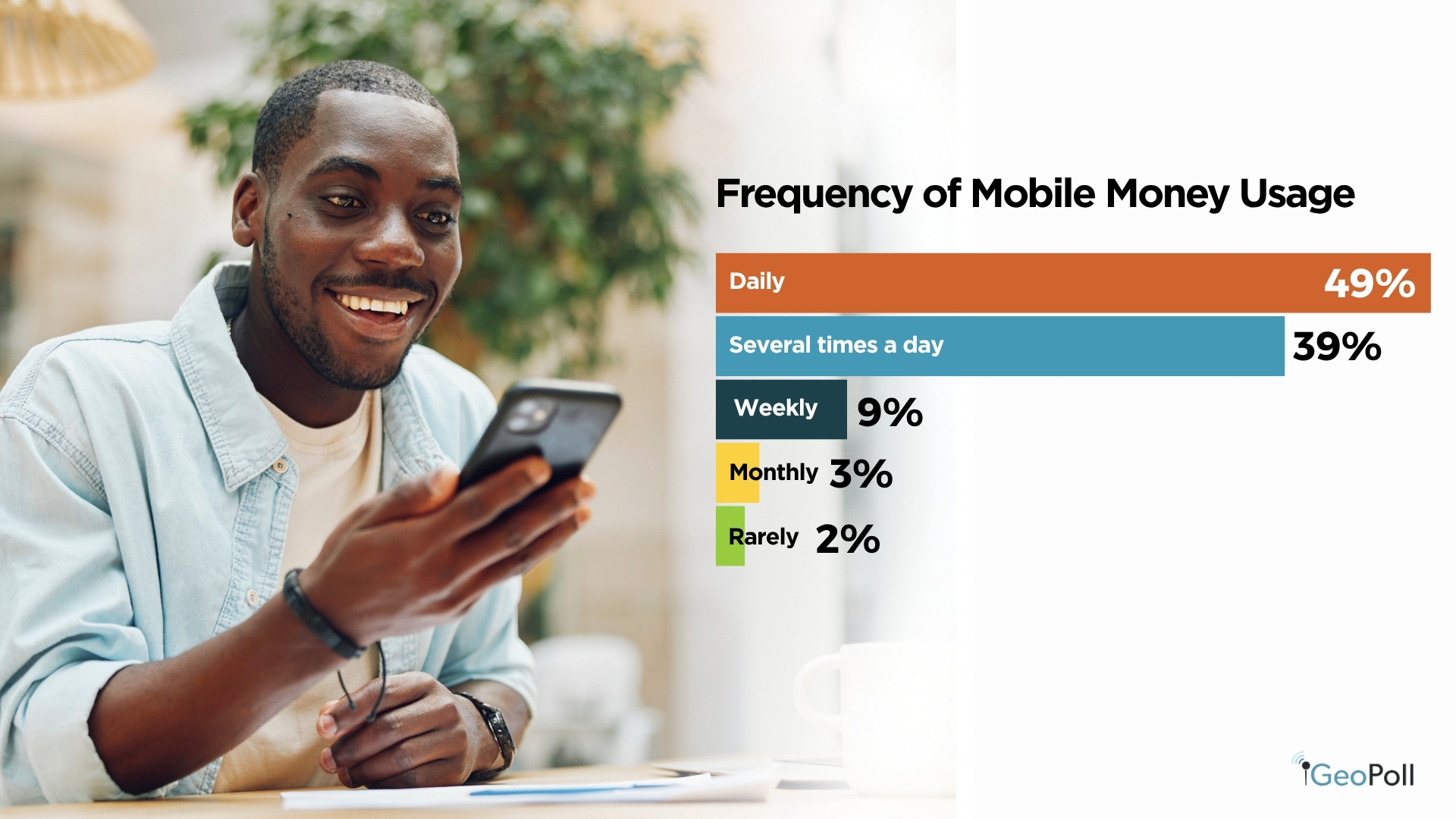
By way of frequency of use, engagement is remarkably excessive, 49% of respondents use cell cash day by day, whereas one other 39% transact a number of instances a day. Solely a small minority use it weekly or much less usually. These patterns display how integral cell cash has turn into to on a regular basis life in Kenya, facilitating the whole lot from routine purchases to revenue administration. The findings spotlight a mature and extremely lively digital finance atmosphere, the place comfort, belief, and accessibility drive sustained adoption and frequent utilization.
Financial institution Account Possession and Utilization in Kenya
Banking entry in Kenya stays vital, although not as widespread or actively used as cell cash. The findings present that 83% of respondents have a checking account, whereas 17% don’t. Amongst account holders, 40% keep a financial savings account, 23% have a present or checking account, and 21% maintain each varieties. This means that the majority customers prioritize savings-based merchandise, aligning with Kenya’s rising tradition of economic prudence and long-term planning. Nonetheless, the comparatively excessive share of people with out financial institution accounts highlights the continued significance of other monetary methods resembling cell cash and SACCOs.

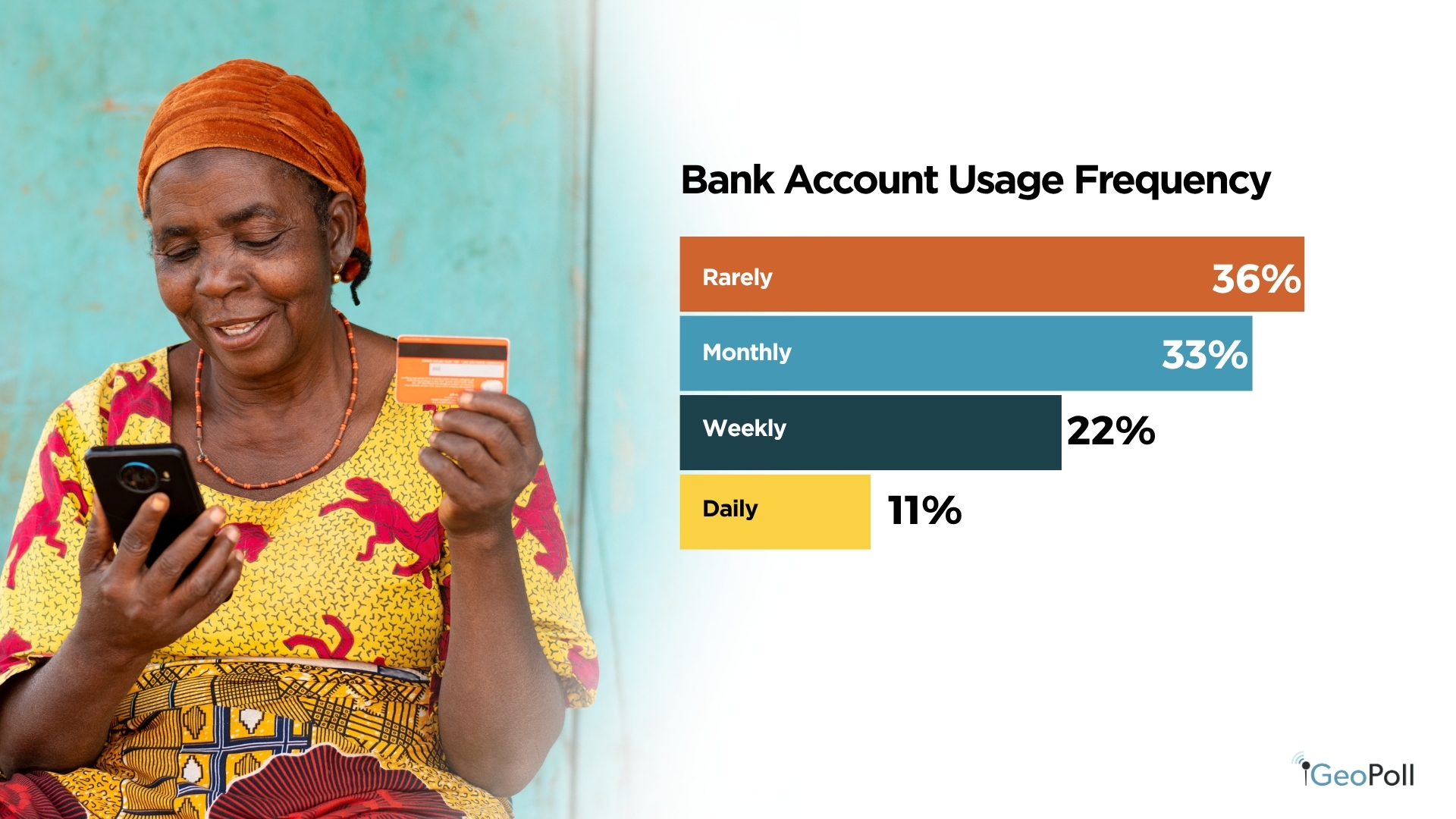
By way of frequency of financial institution use, exercise ranges are average to low. About 36% of respondents use their financial institution accounts not often, whereas one other 33% interact with them month-to-month. Solely 22% entry their accounts weekly, and 11% use them day by day. This implies that whereas many Kenyans keep formal banking relationships, on a regular basis transactions are way more prone to happen by way of cell platforms, which supply better comfort and accessibility for routine monetary wants.
When requested about their principal causes for utilizing financial institution accounts, respondents cited receiving revenue (35%) and saving cash (35%) as the highest functions. Smaller proportions reported utilizing banks to pay payments or faculty charges (8%), conduct enterprise transactions (6%), or entry credit score or loans (4%). These findings present that banks stay trusted for safe deposits and wage dealing with, however are much less built-in into the day by day monetary actions that cell cash now dominates. The info factors to a hybrid monetary atmosphere the place formal banking serves as a basis for financial savings and revenue administration, whereas digital instruments drive on a regular basis monetary interactions.
Prime Banks (% of Mentions)
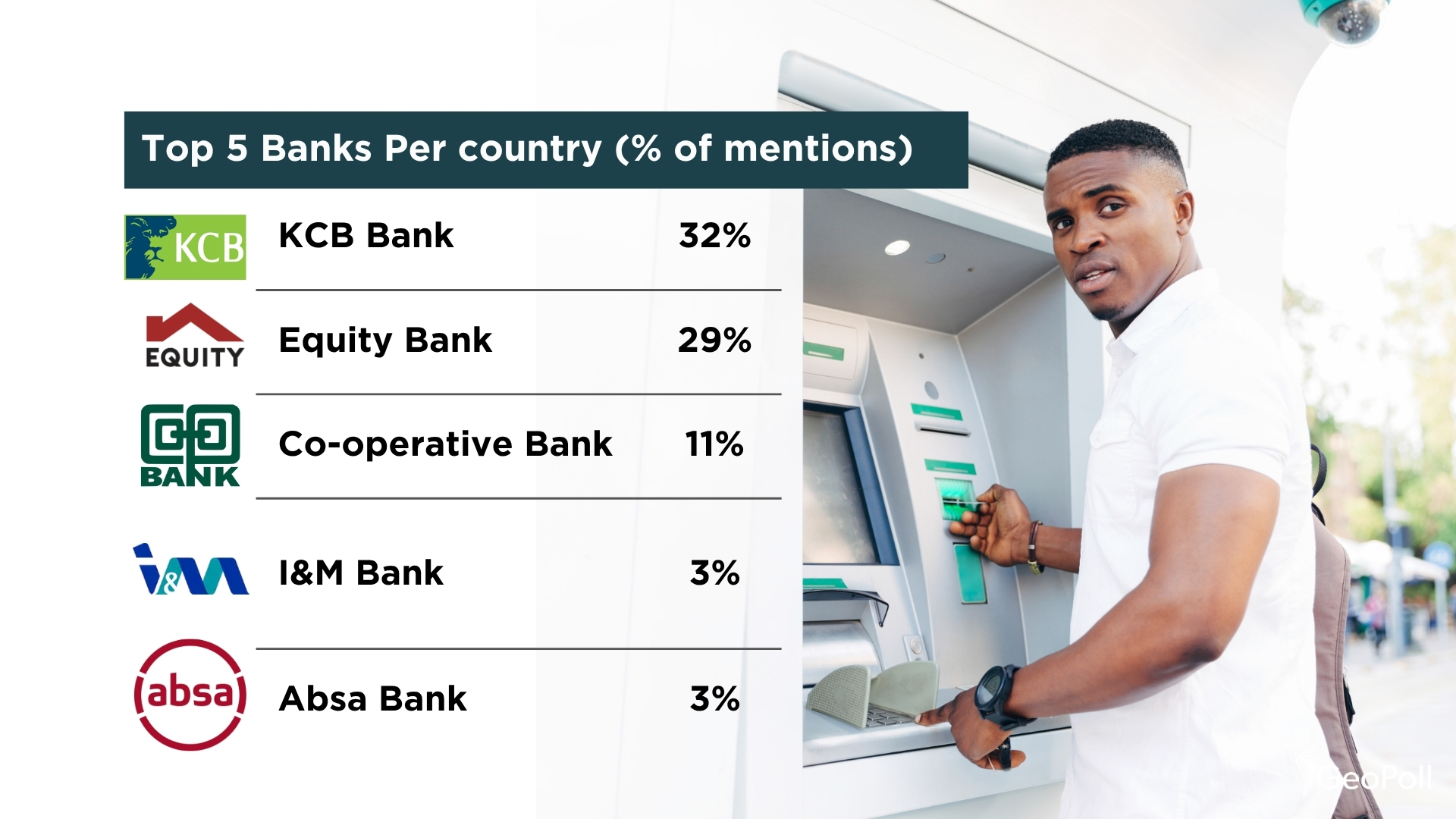
Among the many respondents, the high 5 most popular banks in Kenya are KCB Financial institution (32%), Fairness Financial institution (29%), Co-operative Financial institution (11%), I&M Financial institution (3%), and Absa Financial institution (3%). The outcomes present a robust desire for Kenyan-owned establishments, with KCB, Fairness, and Co-operative Financial institution collectively commanding over 70% of respondents. Their dominance highlights the energy of homegrown banks which have constructed in depth networks and deep group belief, whereas I&M and Absa signify smaller however established gamers throughout the nation’s diversified banking sector.
Borrowing Developments and Mortgage Sources in Kenya
The findings reveal an almost even cut up in borrowing exercise amongst Kenyan respondents. About 47% reported having taken a mortgage previously 12 months, whereas 53% had not. This steadiness means that credit score entry is comparatively widespread however nonetheless moderated by revenue ranges, monetary literacy, or threat aversion.

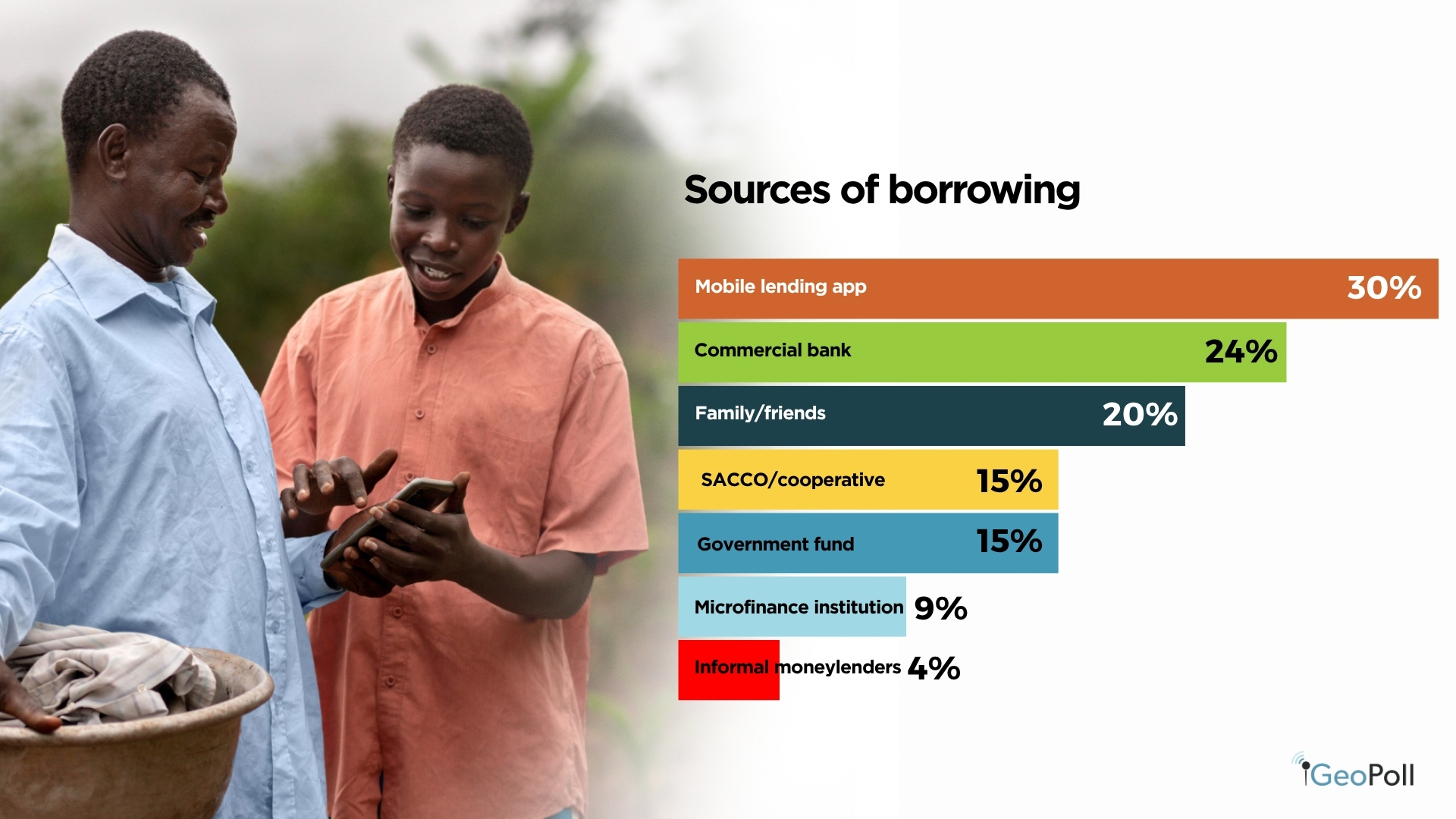
When requested about their sources of borrowing, cell lending apps emerged as the most typical possibility, utilized by 30% of respondents. Their recognition displays the comfort and velocity of digital credit score options like M-Shwari, Tala, and Department. Business banks adopted at 24%, indicating that conventional monetary establishments stay an vital supply of formal credit score, notably for salaried people. Different notable borrowing sources embrace household or pals (20%), SACCOs or cooperatives (15%), and authorities funds (15%), exhibiting a mix of formal and casual mechanisms in Kenya’s credit score panorama. A smaller share borrowed from microfinance establishments (15%) and casual moneylenders (9%), suggesting that whereas entry to credit score is broad, affordability and regulation stay ongoing challenges.
Relating to the principle causes for borrowing, emergencies (27%) topped the record, adopted by enterprise functions (23%) and college or training charges (12%). These patterns spotlight that borrowing in Kenya is basically pushed by short-term wants and income-support actions, slightly than asset acquisition or long-term investments. Fewer respondents cited borrowing for meals (7%), family bills (5%), or asset purchases (4%), reinforcing that loans are sometimes used as monetary buffers slightly than instruments for wealth creation.

Familiarity with Insurance coverage Merchandise
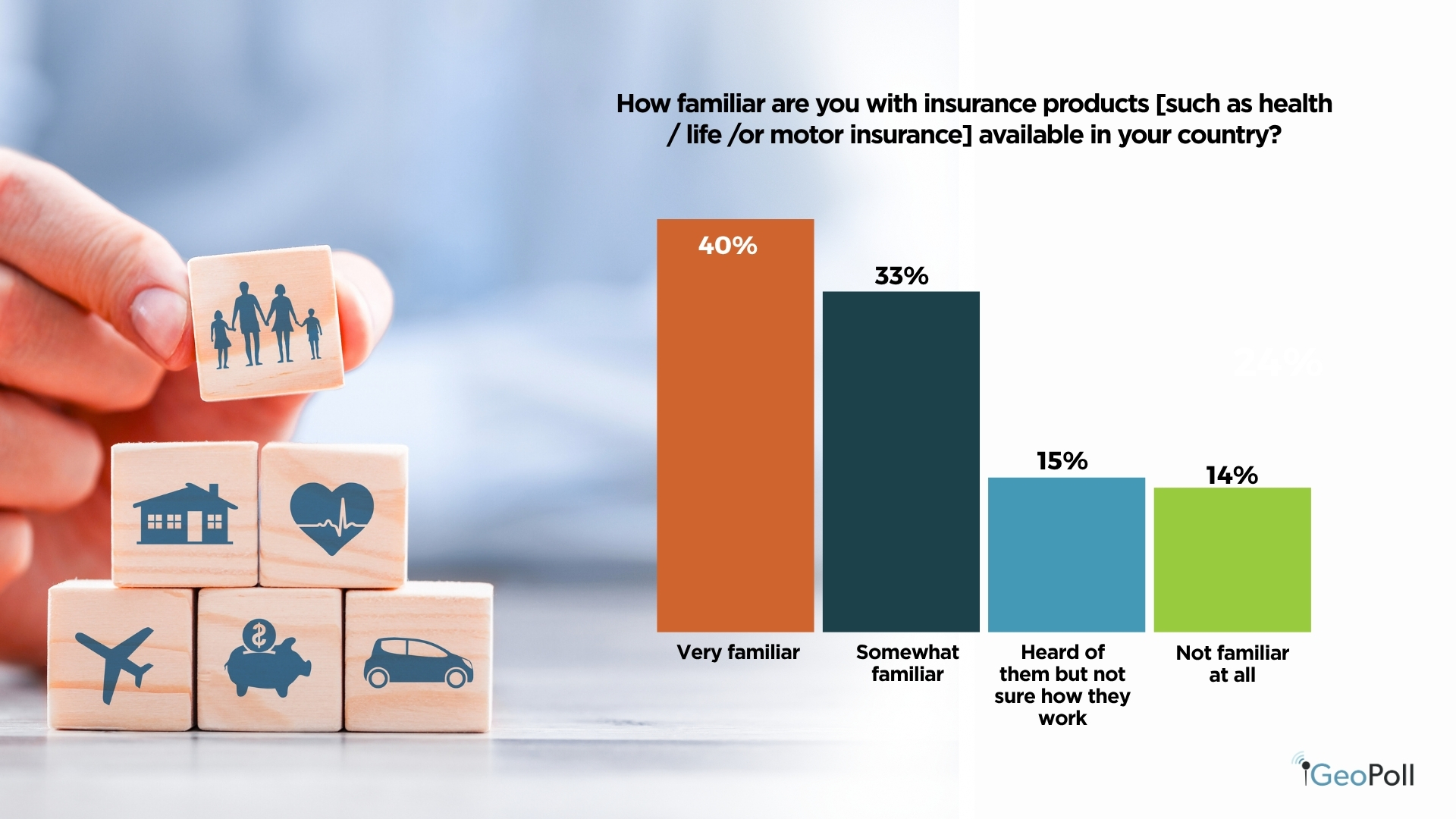
Most Kenyans display a stable consciousness of insurance coverage, with about 40% saying they’re very conversant in totally different insurance coverage merchandise and suppliers. One other 33% are considerably acquainted, exhibiting average understanding. Nonetheless, round 28% have solely heard of insurance coverage or should not acquainted in any respect, indicating that whereas consciousness is widespread, deeper understanding stays restricted throughout parts of the inhabitants.
Insurance coverage Uptake and Protection Sorts
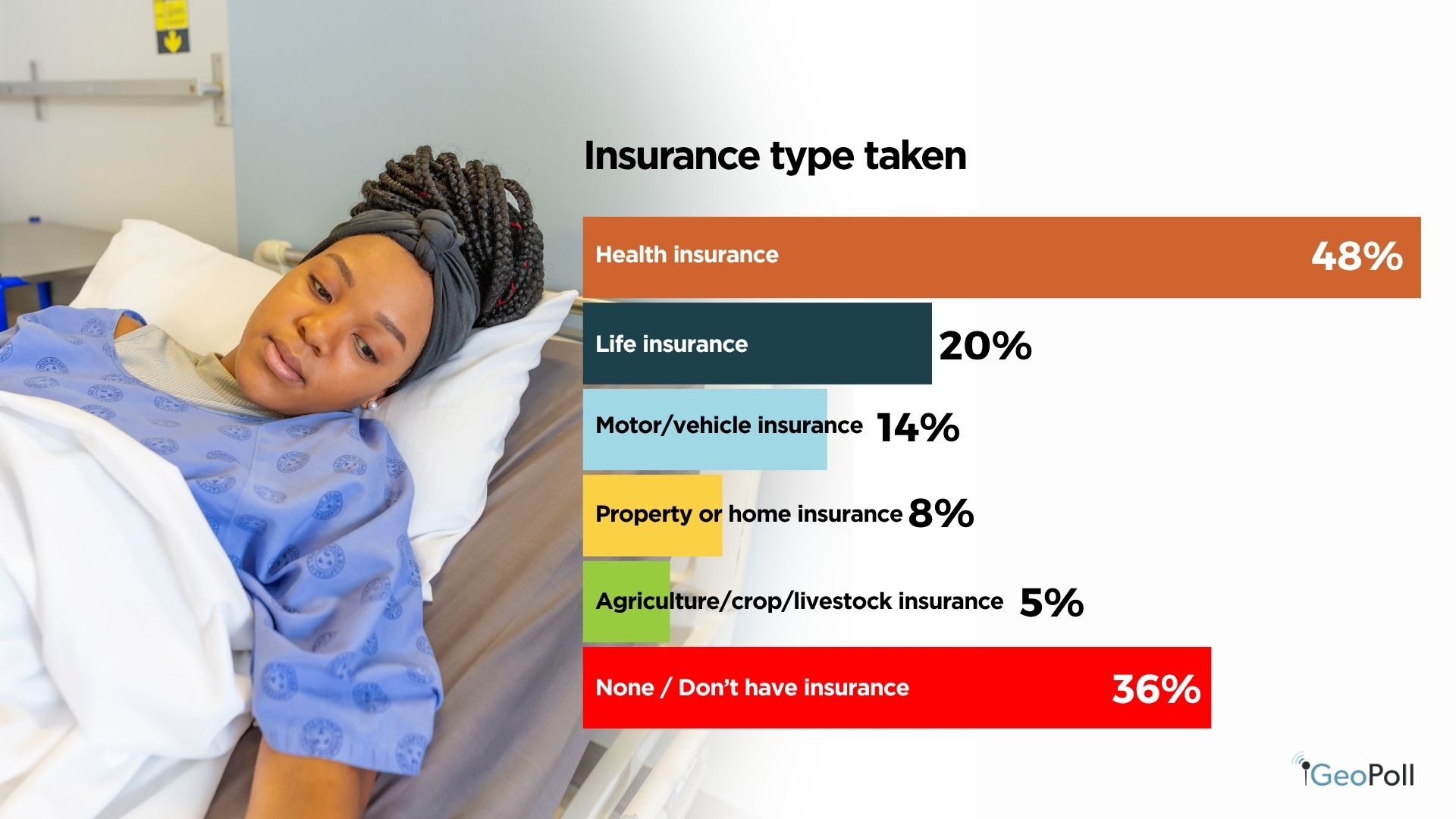
Practically half of respondents, 48%, reported having taken an insurance coverage coverage, whereas 53% stated they haven’t. Amongst these insured, medical health insurance dominates at 48%, adopted by life insurance coverage at 17% and motor insurance coverage at 14%. Round 36% of respondents at present don’t have any insurance coverage protection, revealing vital alternative for development in different classes resembling property, agricultural, and residential insurance coverage.
Boundaries to Insurance coverage Uptake
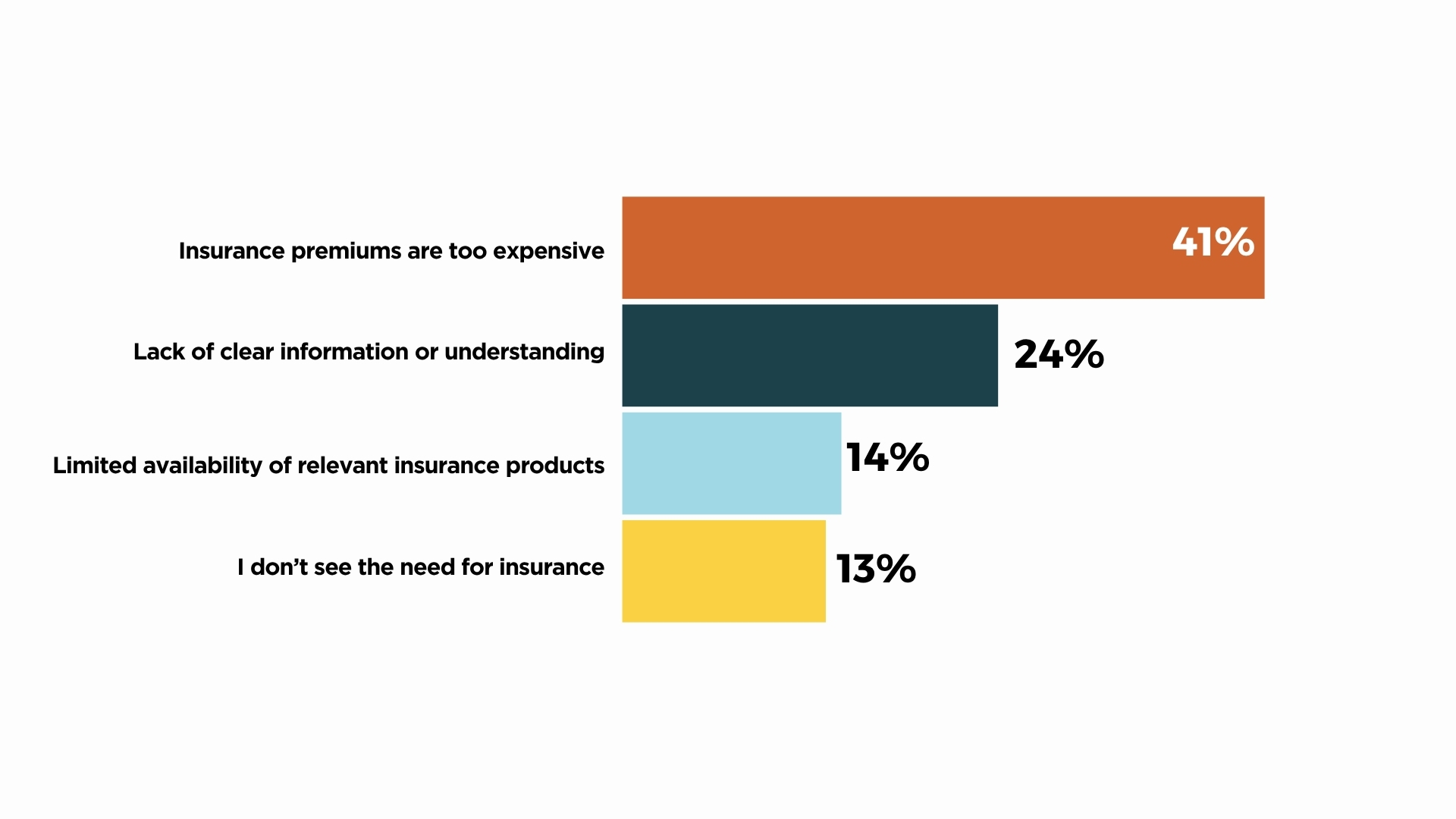
The principle problem limiting insurance coverage adoption is affordability, with about 41% citing excessive premiums as the most important deterrent. One other 24% pointed to lack of clear info or understanding, whereas 14% talked about restricted product availability. Roughly 13% stated they don’t see the necessity for insurance coverage. These findings spotlight the necessity for extra reasonably priced, clear, and accessible insurance coverage choices tailor-made to Kenyan shoppers.
Belief in Insurance coverage Firms
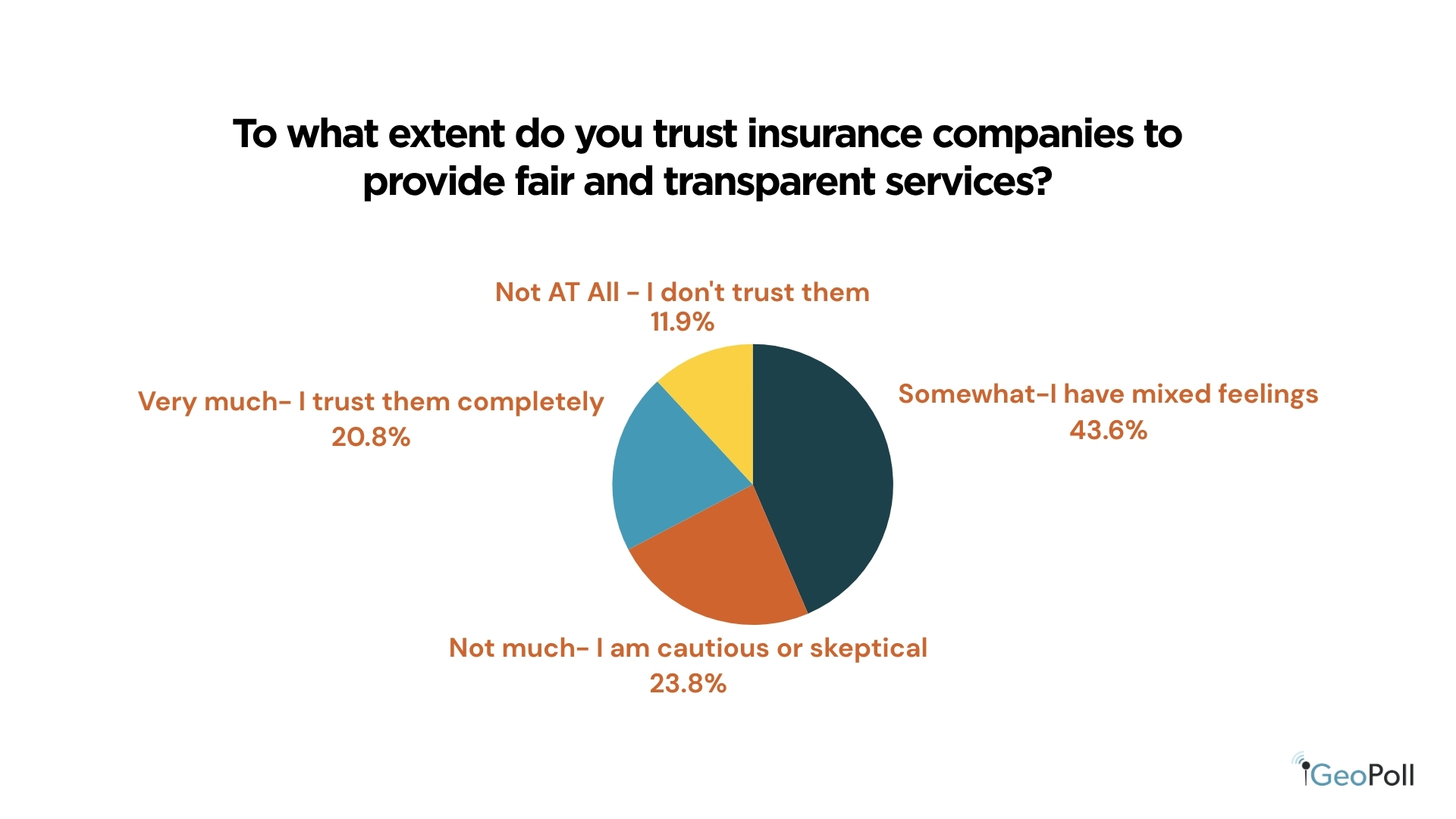
Belief ranges in insurance coverage firms are average. About 44% of Kenyans have combined emotions, 24% are cautious or skeptical, and 21% totally belief insurers. Solely 12% say they don’t belief them in any respect. These outcomes present that whereas consciousness is rising, confidence stays restricted, highlighting the necessity for insurers to enhance transparency and construct stronger buyer relationships.
Challenges, Boundaries, and Satisfaction with Monetary Providers
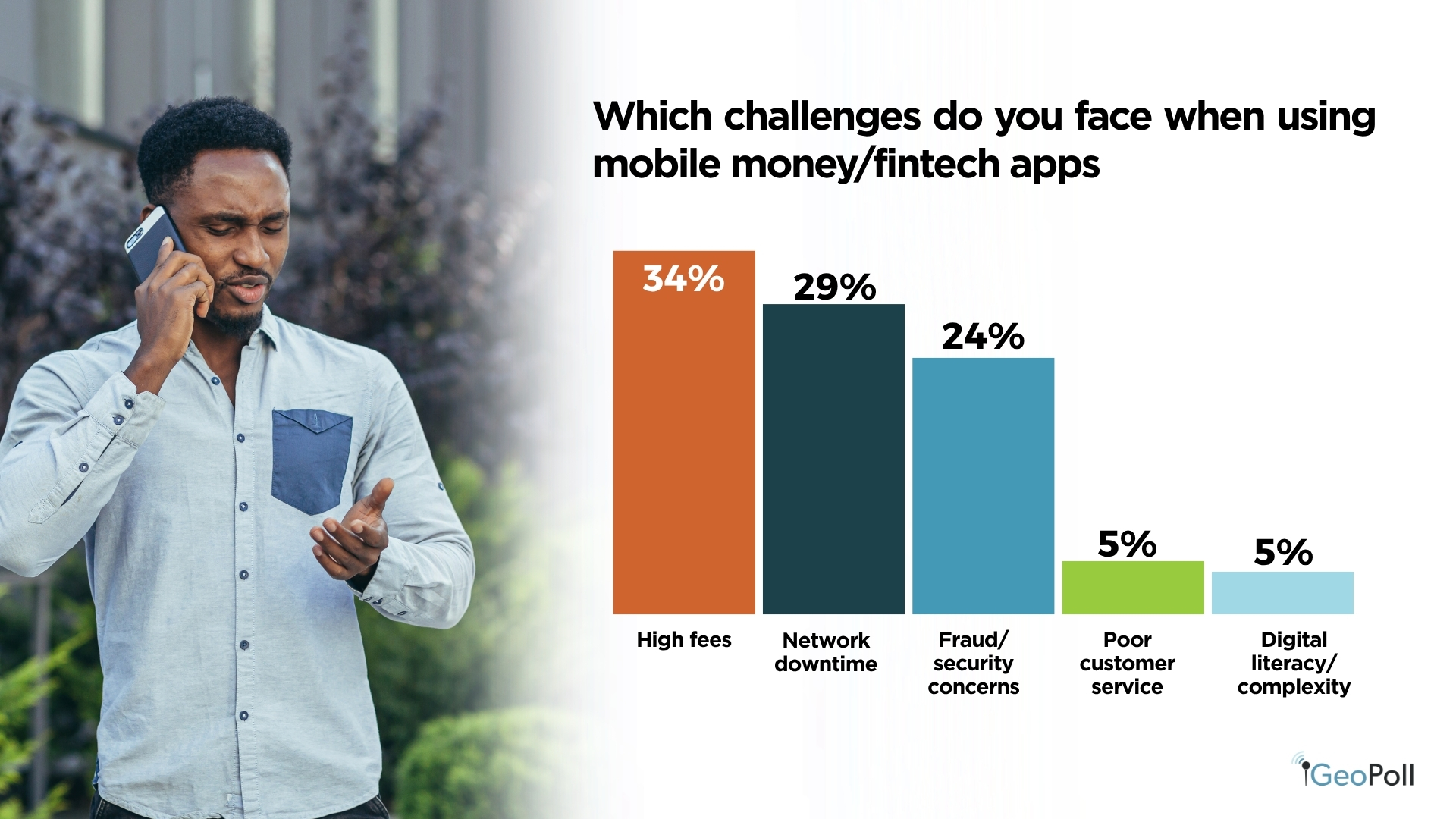
Excessive charges stay a significant concern throughout each cell cash and formal monetary companies, with 34% of respondents citing them as the principle problem in fintech use and 46% figuring out them as the most important barrier to accessing formal monetary methods. Different vital points embrace community downtime at 28% and fraud or safety considerations at 25%, whereas customer support and digital literacy challenges had been reported by fewer customers.
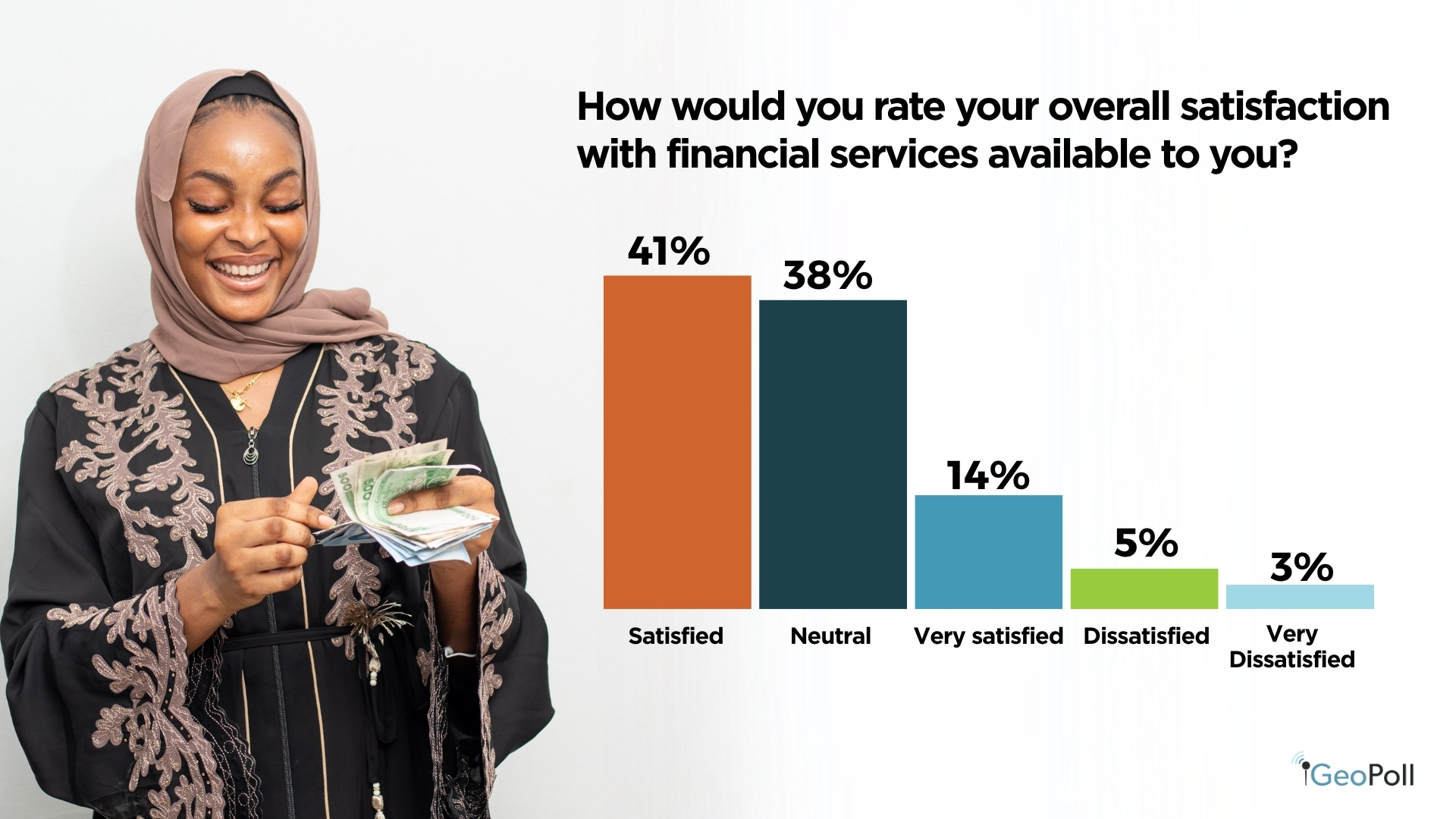
Regardless of these challenges, general satisfaction with monetary companies is pretty optimistic. About 41% of respondents reported being glad and 14% very glad, whereas 38% had been impartial. Solely a small proportion, roughly 8%, expressed dissatisfaction. This implies that though prices and repair reliability are key ache factors, most customers acknowledge some degree of satisfaction with obtainable monetary companies.
When requested about enhancements that might encourage extra frequent use, almost 45% of respondents known as for decrease charges. Higher customer support and simpler entry to branches or brokers had been additionally seen as vital by 20% and 19%, respectively. These insights spotlight a transparent demand for affordability, comfort, and improved service supply to reinforce engagement with monetary merchandise in Kenya.

Monetary Constraints and Main Life Choices
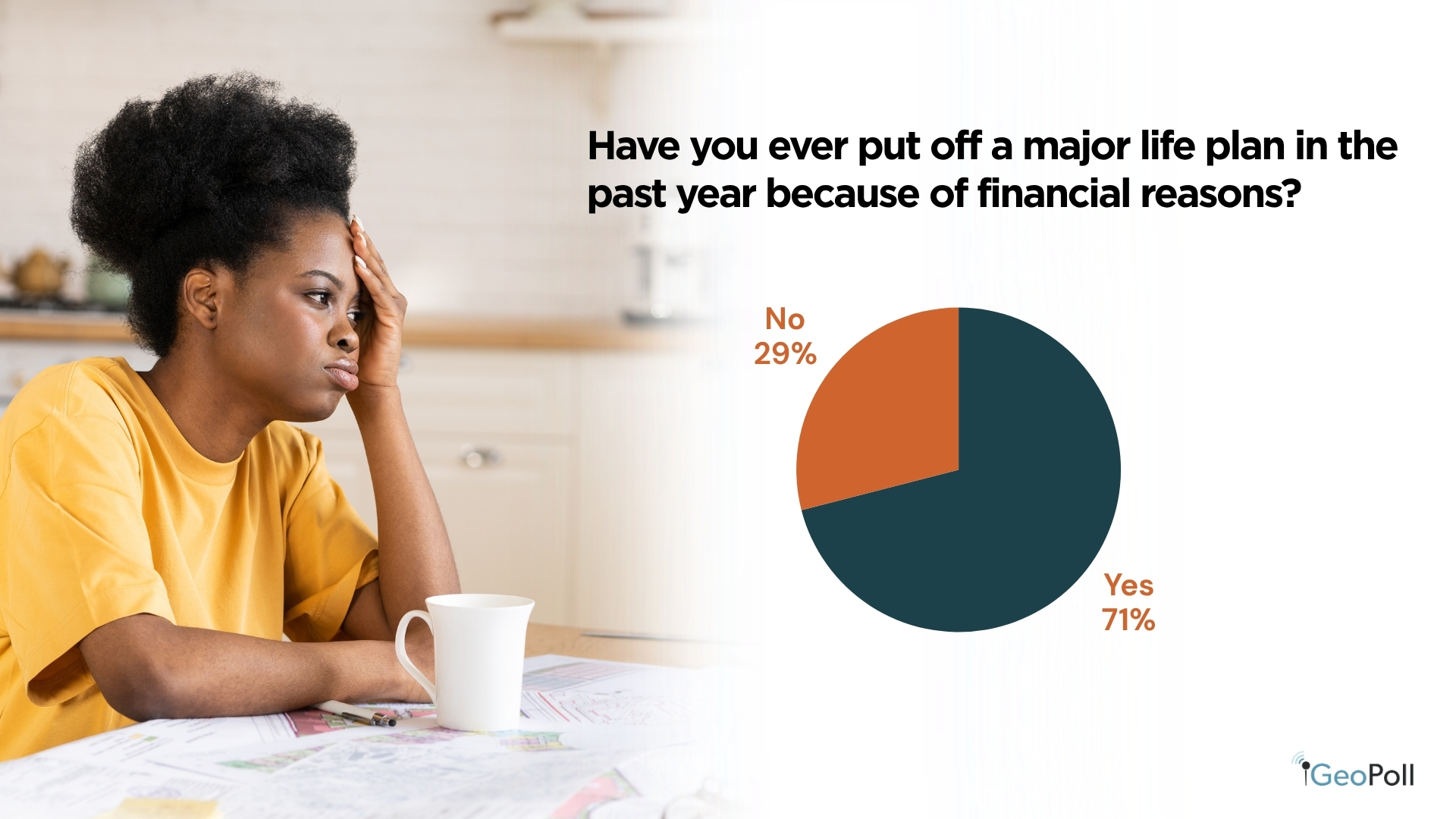
A big majority of respondents, 71%, reported suspending main life plans resembling marriage, training, or beginning a enterprise attributable to monetary causes. Solely 29% stated that they had not delayed any main plans. This means that monetary challenges stay a big barrier to private progress for a lot of Kenyans, affecting long-term objectives and general financial well-being.
Shopper Spending Changes
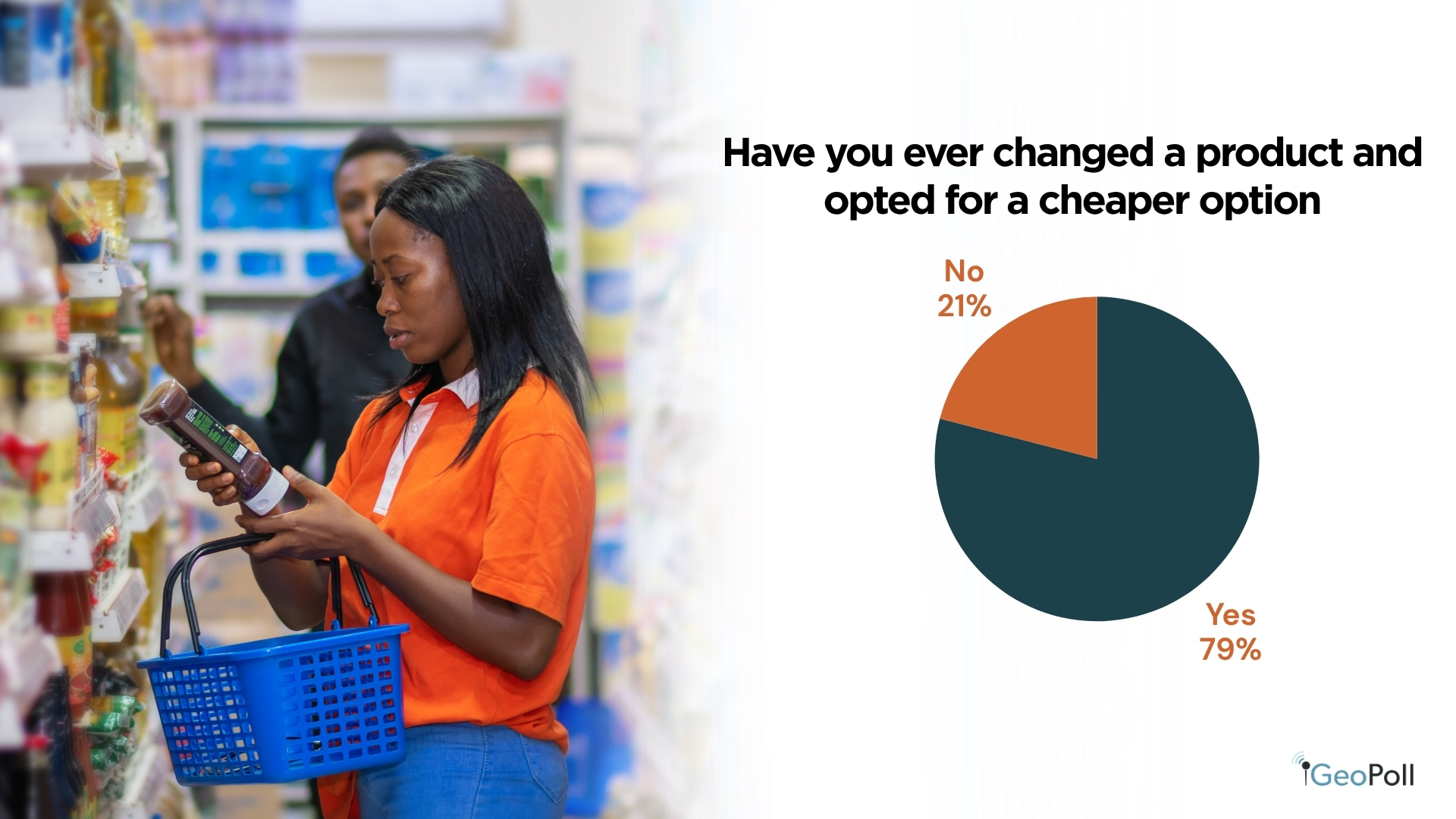
A big 79% of respondents reported altering a product and choosing a less expensive different, whereas solely 22% stated that they had not. This reveals that the majority Kenyans are making cost-conscious selections, doubtless influenced by financial pressures and the rising price of residing, as they prioritize affordability over model or high quality preferences.
Conclusion
Kenya’s monetary panorama continues to set the tempo for digital innovation in Africa, but clear gaps stay between entry, affordability, and depth of use. With 84.8% of adults now financially included and cell cash reaching 98% penetration, Kenya has achieved outstanding progress in increasing entry to monetary instruments. Nonetheless, challenges persist: 41% of respondents cite excessive charges as the principle barrier to insurance coverage and monetary service uptake, whereas 44% specific solely average belief in insurance coverage suppliers.
Monetary pressure stays widespread, with 71% of Kenyans delaying main life selections attributable to cash constraints and 79% choosing cheaper merchandise to deal with rising prices. Regardless of these pressures, 55% of customers report being glad or very glad with obtainable monetary companies, proof of a inhabitants that continues to be resilient, adaptive, and optimistic. Transferring ahead, Kenya’s monetary ecosystem should prioritize affordability, transparency, and accountable innovation to make sure that its digital success story interprets into sustainable monetary well-being for all.
Methodology/About this Survey
This Unique Survey was powered by GeoPoll’s AI platform; Tuucho run by way of the GeoPoll cell software and Cellular internet in Kenya, the pattern measurement was 2,500, composed of random customers between 18 and 50. Because the survey was randomly distributed to an prosperous viewers the outcomes are barely skewed in direction of youthful respondents.
These insights spotlight not solely the evolving nature of Kenya’s monetary panorama, but in addition the ability of GeoPoll in uncovering significant, data-driven narratives throughout various populations. Via its sturdy mobile-based survey expertise and in depth attain throughout rising markets, GeoPoll delivers quick, dependable, and actionable monetary information that helps organizations, policymakers, and researchers perceive shopper conduct, monetary inclusion, and financial tendencies in actual time. As digital finance continues to remodel entry and utilization throughout Africa, GeoPoll stays on the forefront, bridging the hole between folks and insights, and enabling smarter selections by way of a deeper understanding of economic realities.
Please get in contact with us to get extra particulars about our capabilities, discover extra on numerous matters in Africa, Asia, and Latin America.


