The Downside with Conventional Grid Buying and selling
Grid buying and selling is among the hottest methods amongst retail merchants due to its simplicity. A grid EA locations purchase and promote orders at fastened value intervals, aiming to revenue from market fluctuations no matter course.
Nevertheless, the largest weak point of conventional grid techniques can be their defining function: they open trades blindly, with out understanding market construction, pattern course, or momentum.
This method works briefly in ranging markets, however it behaves like playing throughout sturdy tendencies. When value strikes aggressively in a single course, blind grids maintain including shedding positions, resulting in extreme drawdown or full account wipeout.
The true downside is just not grid buying and selling itself — the issue is utilizing grids with out market intelligence.
Why Grid Buying and selling Acquired a Dangerous Repute
Grid buying and selling is usually criticized as a result of many implementations ignore market context. In sturdy tendencies, a grid that retains averaging towards value can accumulate massive floating losses in a really quick time.
This habits has led to the notion that grid techniques are inherently unsafe. In actuality, most failures come from poor management logic, not from the grid idea itself.
A grid is just a place administration methodology. With out course, filters, or limits, it behaves randomly. With construction and guidelines, it turns into predictable.
The repute downside comes from how grids are used — not what they’re.
Ranging vs Trending Markets: Why Context Issues
Markets don’t behave the identical manner always.
In ranging circumstances, grids can carry out properly as a result of value naturally oscillates between help and resistance ranges. In trending circumstances, nevertheless, the identical grid logic can change into harmful if it continues so as to add positions towards momentum.
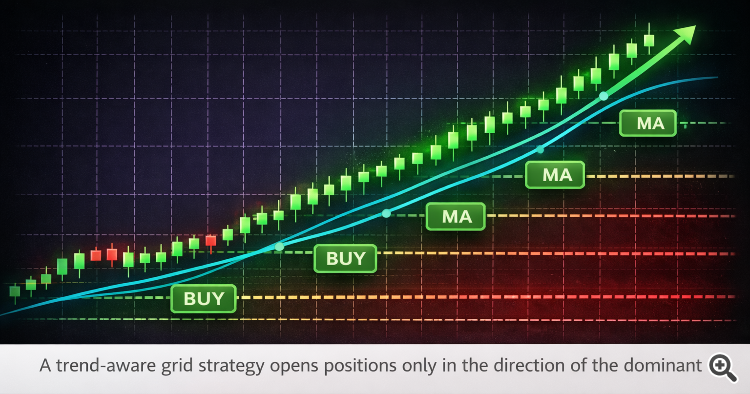
A trend-aware grid technique first classifies market state:
- Vary
- Weak pattern
- Robust pattern
Primarily based on this classification, the system can:
- Allow grids
- Limit grids to 1 course
- Cut back place dimension
- Pause buying and selling fully
This easy context verify dramatically adjustments long-term survivability.
Including Market Intelligence to Grid Buying and selling
A contemporary grid technique doesn’t have to guess. It may observe, filter, and align with the market earlier than inserting any grid orders. As a substitute of opening grids mechanically, a wise grid system first solutions three crucial questions:
-
Is the market trending or ranging?
-
What’s the dominant course?
-
Is momentum sturdy sufficient to justify new positions?
That is achieved by integrating pattern detection and technical indicators straight into the grid logic.
1. Development-Aligned Grids As a substitute of Bidirectional Playing
Fairly than opening each purchase and promote grids on the identical time, a trend-aware grid system:
-
Opens buy-only grids in bullish circumstances
-
Opens sell-only grids in bearish circumstances
-
Avoids buying and selling fully when circumstances are unclear
Widespread instruments used for this embrace:
This single change dramatically reduces drawdown throughout sturdy market strikes.
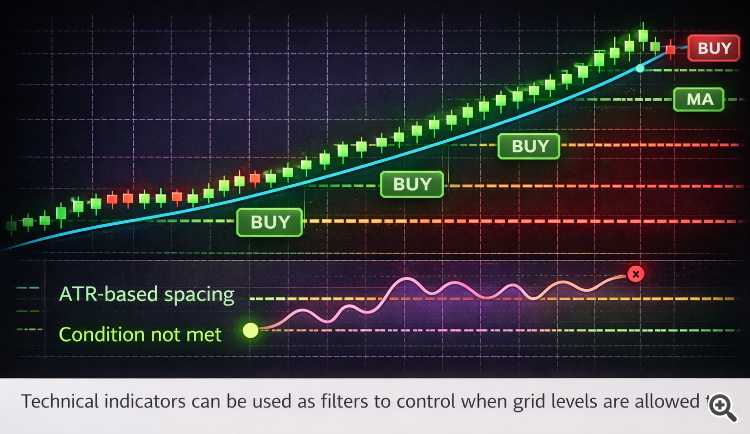
2. Indicator-Filtered Grid Entries
Grid spacing alone is just not sufficient. Good grid techniques use indicators as entry filters, not alerts.
Examples:
-
RSI or momentum indicators to keep away from shopping for into overbought circumstances
-
Volatility filters to stop grids throughout excessive market spikes
-
ATR-based spacing to adapt grid distance dynamically to market circumstances
This transforms the grid from a static lure right into a responsive system that adapts to market habits.
3. Conditional Grid Growth As a substitute of Fastened Layers
Conventional grids maintain including positions it doesn’t matter what. A contemporary grid system expands solely when:
If circumstances change, the system can:
-
Pause new grid ranges
-
Cut back place dimension
-
Shut publicity early
This makes the grid behave extra like a skilled position-management instrument slightly than a martingale.
Threat Management: The Lacking Layer in Most Grid Techniques
Many grid methods fail as a result of threat is managed implicitly slightly than explicitly. A contemporary grid system ought to outline:
-
Most variety of grid ranges
-
Most whole publicity per image
-
Most acceptable drawdown
-
Circumstances for pressured shutdown
When mixed with pattern and indicator filters, these limits forestall grid growth from turning into uncontrolled averaging. Threat management doesn’t scale back profitability — it ensures the technique can keep available in the market lengthy sufficient to be worthwhile.
From Playing Logic to System Logic
Grid methods fail once they assume the market will all the time return. They succeed once they function below the belief that generally it won’t.
By incorporating pattern evaluation, indicator affirmation, and strict threat boundaries, grid buying and selling shifts from hope-based logic to system-based determination making.
Conclusion
Grid buying and selling doesn’t must be reckless.
By combining pattern evaluation, technical indicators, and adaptive logic, grid methods can evolve from high-risk playing instruments into managed, rule-based buying and selling techniques.
A sensible grid technique:
-
Trades with the market, not towards it
-
Reduces pointless drawdown
-
Avoids catastrophic pattern publicity
-
Behaves predictably below stress
The way forward for grid buying and selling is just not about including extra orders — it’s about including higher selections earlier than inserting them.
Grid buying and selling isn’t useless. Blind grid buying and selling is.


