When a founder sells their firm, its valuation will get a variety of consideration. However an excessive amount of emphasis on valuation typically results in too little consideration for what stockholders and stakeholders pay in taxes post-sale.
After an exit, some founders might pay a 0% tax whereas others pay over 50% of their sale proceeds. Some founders can stroll away with as a lot as two instances the cash as different founders on the identical sale worth — purely because of circumstances and tax planning. Private tax planning can in the end impression a founder’s take-home proceeds as a lot as exit-level valuation adjustments can.
How does this occur? Taxes owed will in the end rely on the kind of fairness owned, how lengthy it’s been held, the place the shareholder lives, potential tax fee adjustments sooner or later and tax-planning methods. When you’re eager about taxes now, likelihood is you’re forward within the sport. However figuring out how a lot you’ll owe isn’t easy.
On this article, I’ll present a simplified overview of how founders can take into consideration taxes in addition to a straightforward technique to estimate what they’ll owe in tax upon promoting their firm. I’ll additionally contact on superior tax planning and optimization methods, state tax and future tax dangers. After all, keep in mind that this isn’t tax recommendation. Prior to creating any tax selections, it is best to seek the advice of together with your CPA or tax adviser.
How shareholders are taxed
In relation to minimizing capital positive factors tax, QSBS (certified small enterprise inventory) generally is a game-changer for those who qualify.
Let’s assume you’re a founder and personal fairness or choices in a typical venture-backed C-corp. Quite a few elements will decide whether or not you’ll be taxed at short-term capital positive factors (atypical earnings tax charges) or long-term capital positive factors, additionally known as certified small enterprise inventory (QSBS) charges. It’s important to grasp the variations and the place you possibly can optimize.
Under is a chart summarizing various kinds of taxation and when every applies. I additional break this down to point out the mixed “all in” federal + state + metropolis taxation, if relevant.
Founders with exits on the horizon that can increase greater than $10 million ought to discover a few of the superior tax methods I lined in one among my earlier articles, since there are alternatives to multiply or “stack” the $10 million QSBS exclusion and reduce taxation additional.
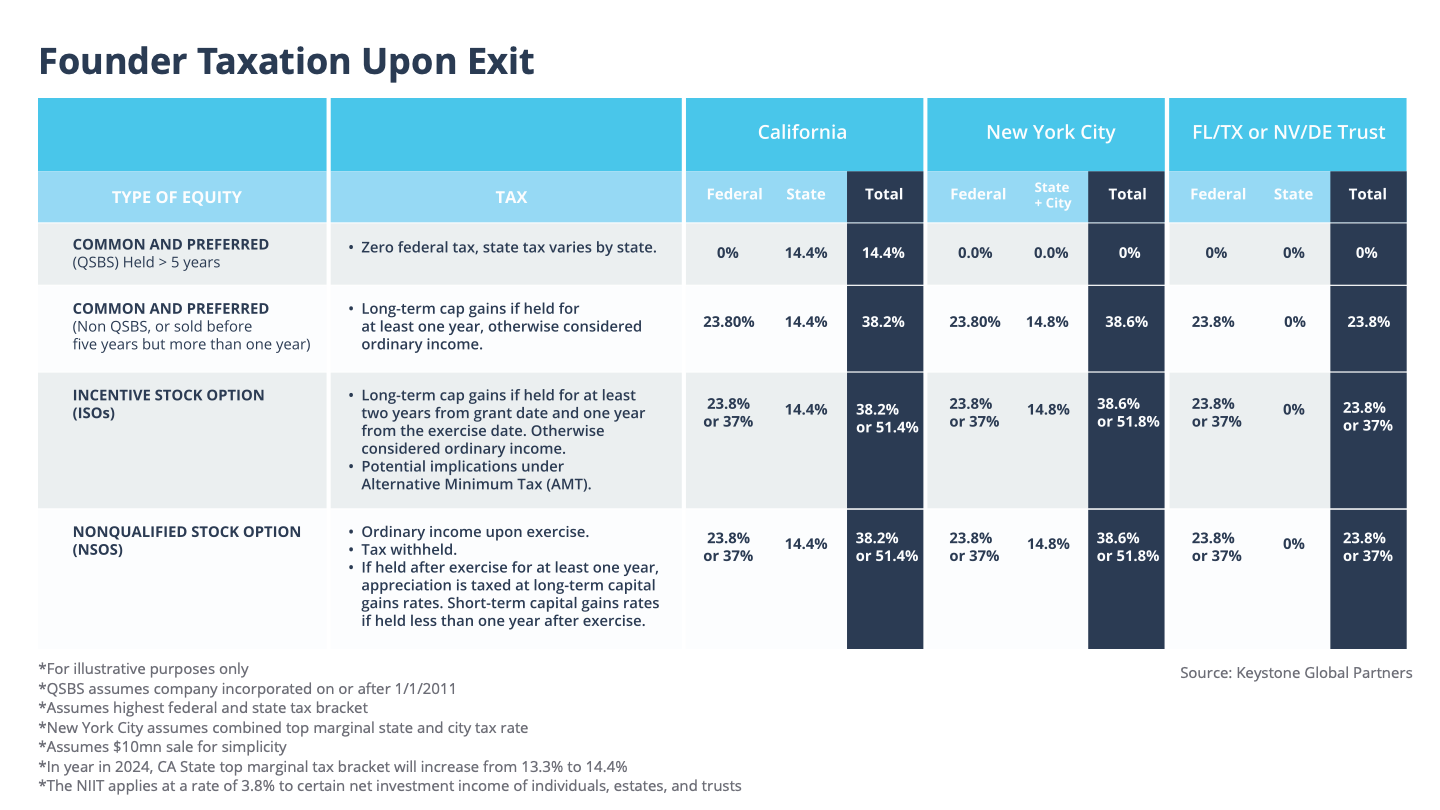
Picture Credit: Keystone International Companions
As you possibly can see above, a few of the extra widespread levers that affect how a lot tax a founder owes after an exit embrace QSBS, belief creation, which state you reside in, how lengthy you’ve held your shares and whether or not you train your choices.


